Description
Inaccurate blur estimation may occurs at weak edges, noise or soft features. We solve this problem by applying joint bilateral filtering (JBF) on the edge locations. Sparse defocus map is obtained from input fig1.a and here we compare the results before and after applying JBF. Fig. 1b) shows many bright colored spots randomly distributed across the whole image.
After applying JBF (fig. 1c), those errors are almost completely removed from the defocus map while edges are well preserved. Thus, JBF is very effective to smooth the sparse defocus map and prevent errors propagate in the step of interpolation.
We applied different methods on the sparse defocus map to obtain the full defocus map. It can be seen from original image (fig. 2a) that the two pumpkins at the lower part of the image have much sharper edges compared to the others. After that, full defocus maps were obtained by using nearest neighbor method (fig. 2b) and matting laplacian (fig. 2c).
Both estimated full maps can capture continuous change of depth. The nearest neighbor method produce coarse defocus map and the pumpkins are not well separated with the background. In contrast, matting laplacian method is able to produce a more accurate defocus map.
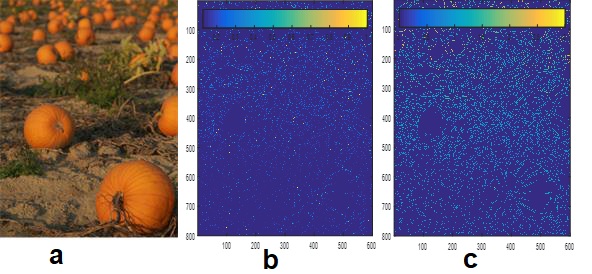
a) input image and sparse defocus maps before (b) and after (c) applying the bilateral filter

Obtain defocus map from input image a) by applying nearest neighbor method b) and matting laplacian c). Matting laplacian results in defocus map with good accuracy.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.