Description
A medical diagnosis is the process of trying to identify a disease or disorder through one or several techniques aimed at reaching a medical diagnostic opinion.
There are numerous methods for diagnosing a disease, including clinical diagnosis, radiology diagnosis, and laboratory diagnosis, often used in concert, with each having the potential to be an effective tool in reaching a definitive diagnoses. For example, a doctor may have an idea of what his/her patient’s ailment may be on the basis of observable medical signs and patient reported symptoms, and confirm the initial diagnostic opinion with a laboratory test before proceeding with treatment. Laboratory diagnostics are invaluable in the medical field now more than ever, thanks to the proliferation of biomarker identification and genetic testing, which promise to identify disease before it could otherwise be detected using classical forms of diagnostics . Diseased but asymptomatic patients are unlikely to be diagnosed unless they receive regular blood workups testing for biomarkers linked to that particular disease. Testing of this type is important because early diagnosis often significantly increases a patient’s survival rate and decreases the overall cost of the treatment received.
The WHO defines a biomarker as “almost any measurement reflecting an interaction between a biological system and a potential hazard, which may be chemical, physical, or biological. The measured response may be functional and physiological, biochemical at the cellular level, or a molecular interaction.” . The purpose of this investigation is to use proteins present in human blood as the laboratory-measured biomarker for various diseases, biomarkers that have a relationship to relevant clinical endpoints . One such example of using a biomarker
as a quantifiable characteristic of a biological process is the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease by measuring the level of mutant amyloid proteins called prions , or possibly a close relative of the beta-amyloid protein itself . An example of a more clinically recognized protein biomarker is human C-Reactive Protein (CRP), produced as part of the nonspecific acute-phase response to most forms of inflammation, infection, and tissue damage . Not only are CRP levels elevated after a cardiac event, but studies show that there is a predictive aspect to elevated CRP levels before an atherothrombotic event, including coronary events, stroke, and progression of peripheral arterial disease . CRP has also proven to be one of the most sensitive and responsive biomarkers present in human blood, thus necessitating a rapid test allowing medical personal to take multiple CRP concentration measurements in the time that would have previously only allowed one measurement, thus allowing a faster response time for treatment. This is one area that a microfluidic POC device could thrive.
Objective
This investigation seeks to develop a portable, microfluidic fluid handling system designed to rapidly detect protein biomarkers in whole human blood. The detection system is based on a fluorescent heterogeneous assay developed and benchmarked using C-Reactive Protein in buffer. The problem entails integrating and further developing individual methods and components previously tested , as well as novel methods and components, in order to yield a functioning Point-of-Care (POC) device.
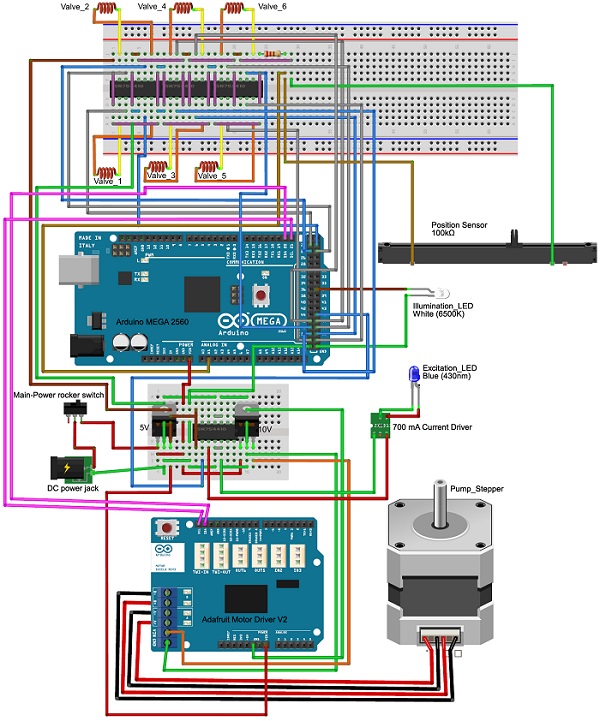
Wiring diagram of the components used in the portable device
The portable unit used two control systems, the Arduino MEGA located inside the device and a MATLAB function that ran on a separate personal computer (PC). The Arduino was connected to the PC through serial communication over a connected USB cable, and commands were sent between MATLAB and the Arduino during the course of a test. Each control system had their own duties, but ultimately, the MATLAB function held a superior position because it controlled when the Arduino would carry out its duties. For example, a valve configuration would be triggered when the MATLAB function sent a particular character over serial communication to the Arduino, and once received, the Arduino would run a particular subroutine activating the desired valve configuration depending on the character received.
MATLAB and Arduino C++ code for microfluidic DNA analysis systems



Devansh –
It was professional. I would like to appreciate your work.