Description of a Digital Image Processing System
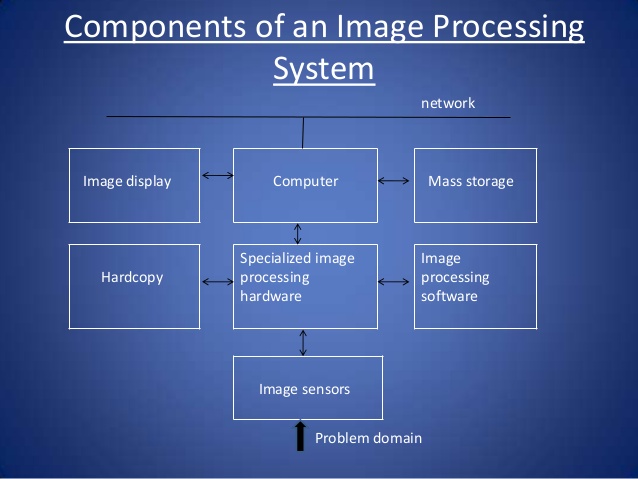
There are many parts involved in processing an image. Figure 6 illustrates the components involved in the digital image processing system. The following list explains each art present in Figure 6.
Sensor : The initial part of a digital image processing system is the sensor that is responsible for obtaining the image from the environment and digitizing it into a format compatible for processing by a digital computer.
Specialized digital image processing hardware : Here analog images are converted to a digital format. Furthermore, primitive operations such as Arithmetic Logical Unit are performed on the input. These systems are characterized by fast speeds
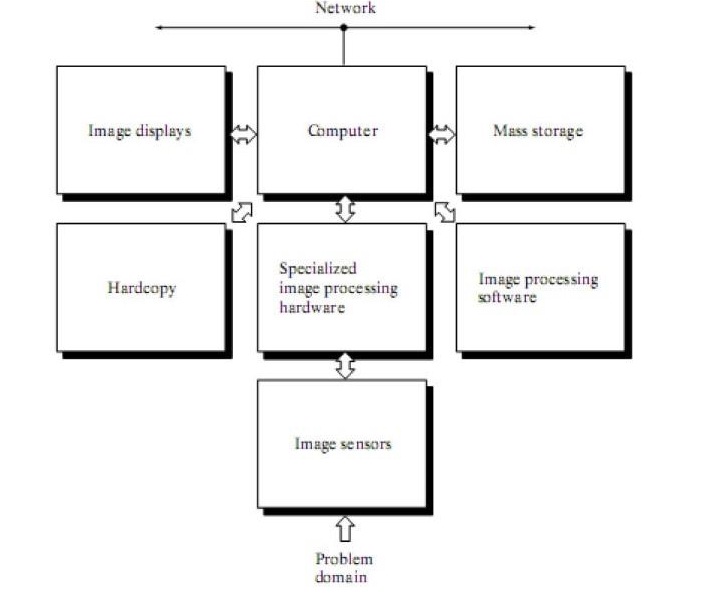
FIGURE 6. Block diagram depicting the components of a digital image processing system
Computer : A computer is the main processing part of the digital image processing system
that performs the computational tasks.
Software : Software consists of specialized modules to perform the digital image processing tasks. They are usually coded in a binary format into the processor.
Mass storage : The images that are processed can be of varying sizes. For example, an image can be 1024 by 1024 pixels, and the intensity of each pixel can be 8 bits. Hence, processing many images of such a size demands a lot of memory. Memory can be in the form of short-term storage such as computer memory or frame buffers.
Image displays : Image displays commonly used are color monitors whose display is derived from graphic or image cards.
Hardcopy : Hardcopy formats that are used to display the output of digital image processing system are paper and image projectors.
Networking : Networking is an important part of today’s digital image processing system, and the key considerations are the bandwidth of transmission as the images require a lot of memory.
Major Steps in Digital Image Processing
The following section is a summary of the steps involved in digital image processing from the input to the output stage. The general flow of the process is displayed in Figure 7.

FIGURE 7. Fundamental steps involved in digital image processing
1. Image acquisition : This step includes obtaining the image in a digital format and performing image pre-processing.
2. Image enhancement : Enhancement requires highlighting features of interest in an image. In addition, obscured parts of the image are improved. Enhancement is dependent upon a human’s judgment in the quality of the image.
3. Image restoration : Restoration involves improving the appearance of an image by employing mathematical and probabilistic methods of image degradation.
4. Color digital image processing : This step involves processing of color images by taking
into consideration the various color models available. The internet forms a major source of color digital images.
5. Morphological processing : This step deals with the tools that extract image components needed to describe and represent the shapes of interest within an image.
6. Image segmentation : Segmentation requires separating an image into components for individual analysis of each component.
7. Representation and description : This step involves presenting the image in a format that is favorable for the computer to carry out processing. The above sections provided a general introduction to the field of digital image processing by discussing the origins, applications, and process involved. The next section introduces the antibiotic susceptibility test. The goal of the proposed project is to automate this test.