Medical Imaging Overutilization
Overutilization of medical imaging services is a healthcare disparity that may not be widely recognized by the healthcare industry, but this issue has known implications on quality, value, and safety of healthcare delivery. Overutilization occurs due to a variety of factors with the majority of these stemming from ordering physician and provider utilization of imaging services. There have been efforts to address medical imaging overutilization that focused control and containment, but medical imaging services continue to be over utilized. Federal healthcare reform has recognized the need to address medical imaging overutilization because of the growing cost and safety concerns that result from excessive and sometimes inappropriate imaging use. Provisions of the Affordable Care Act specifically target medical imaging overutilization, and upcoming reform efforts will be enacted to appropriate the use of medical imaging services. While these efforts will specifically apply to Medicare reimbursement, the ideal is that appropriation of medical imaging services will promote efficacious use of healthcare services throughout the industry to improve quality and safety of care.
Growth of Medical Imaging Services
During the past decade, medical imaging services and their costs have grown at about twice the rate of all other healthcare services For example, between 2000 and 2005, spending on imaging services in the US doubled from $6.6 billion to $13.7 billion
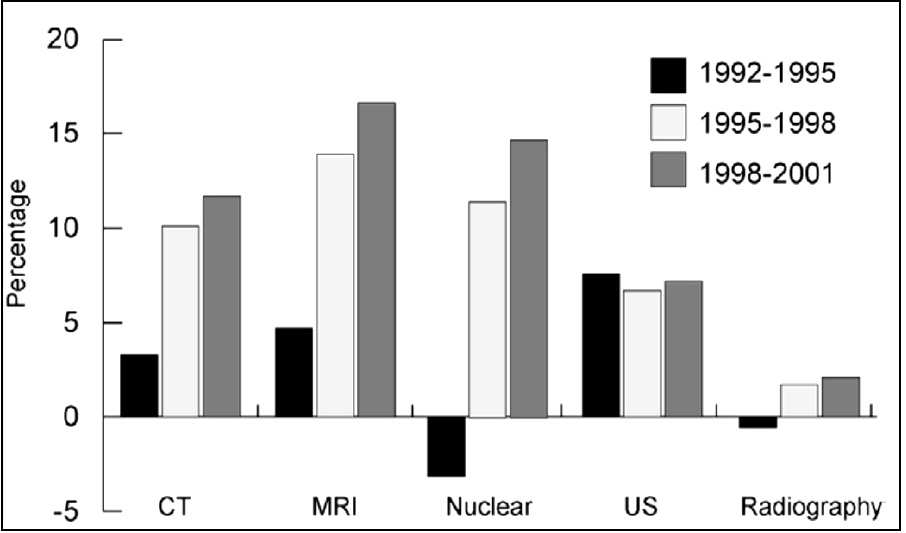
Figure 1. Compound Annual Rate of Increase in RadiologyUtilization. A disproportionate increase in high-cost imaging modalities was seen in the 10-year period between 1992 and 2001. Use of radiography remained relatively flat while CT and MRI increased by double-digit annual rates
Increase in Patient Radiation Doses
Overutilization presents a concern to patient safety for the reason that patients may be exposed to unnecessary radiation doses. explained that overutilization increases the average radiation dose to the population: In 1980, the U.S. annual population dose from medical imaging procedures was 124,000 person-sieverts. In 2006, this dose increased to 880,000 person-sieverts. Today, medical imaging radiation contributes to more than half of the total radiation dose for Americans; where in 1980 it was less than a quarter of the average dose. The ionizing radiation used in many medical imaging modalities – radiography, fluoroscopy, mammography, nuclear medicine, CT, and PET – is known to have potential biological effects
Actions to Address Overutilization
With the passing of the Affordable Care Act, healthcare reform became an area of increase attention for national and healthcare leaders. Medical imaging is one particular field of health care receiving extra scrutiny because research has demonstrated areas of wasteful spending and increased potential for patient harm from unnecessary radiation exposure. Overutilization of imaging services has been identified as the leading cause of medical imaging disparities, with specific contributing factors that drive medical imaging overutilization. In order to effectively address medical imaging overutilization, the contributing factors need to be better understood. Justification for reform is appreciated by exploring the attempts to address medical imaging overutilization that have been previously employed and why these efforts have failed to contain medical imaging growth. Further justification is provided through research regarding the lack of awareness and action by imaging leaders to address overutilization