IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF UNIT COMMITMENT AND ECONOMIC DISPATCH FORMULATIONS
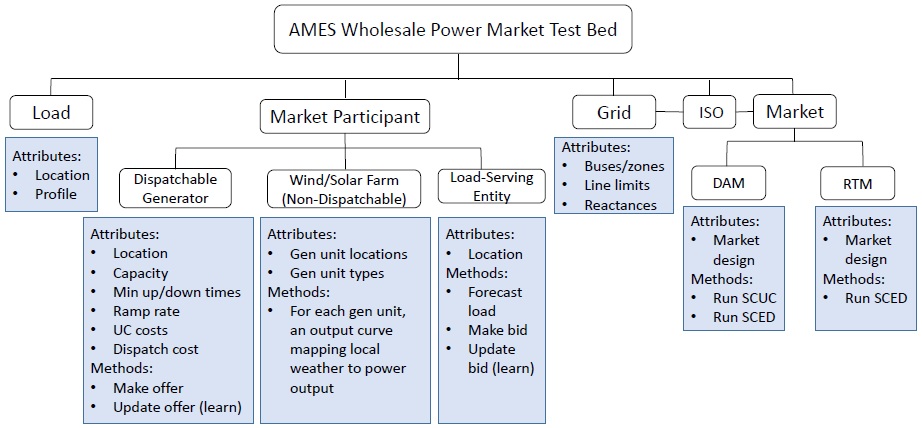
Figure 1. AMES General Agent Hierarchy
Modeling tools demand more efficient and accurate tools to support decision making for resource scheduling in large complex power systems. Market operation problems are solved in power systems to determine when to startup or shutdown generating units, and to decide how to dispatch these generating units to meet system demand and spinning reserve requirements. These decisions are optimized minimizing overall operations cost or maximizing social welfare while under generation constraints like production limits, ramping limits, minimum up times, minimum down times, and system constraints like line limits, voltage limits and angle limits. Generation scheduling problems are solved by Independent System Operators (ISO) in electricity markets, using market participants bids and offers to maximize social welfare. System operators ensure system reliability by utilizing Security Constrained optimization models, namely a unit commitment and economic dispatch model that is extended to include transmission network constraints. Simulating real world operations more accurately or efficiently can result in better decision making tools.
Description of updates to AMES
Significant changes were made to better represent a model of the wholesale power market. These changes will be released as a version update, in the form of AMES (V4.0)1 . The following is a summary of the description of the changes from AMES (V2.06). The full comprehensive list of changes in AMES (V4.0) is described as part of the documentation . 1. AMES (V2.06) employs a DCOPFJ algorithm to solve for optimal dispatches in a Day- Ahead Market (DAM). AMES (V4.0) incorporates a new DAM interface. This DAM interface allows switching between different solvers. The current solvers supported are:
(a) Deterministic and Stochastic SCUC using Pyomo
(b) Deterministic SCUC using PSST and Pyomo
2. AMES (V4.0) also incorporates hourly Real-Time Market (RTM) interface. This RTM interface allows switching between different solvers. The current solvers supported are:
(a) Deterministic SCED using Pyomo
(b) Deterministic SCED using PSST and Pyomo
3. AMES (V4.0) allows the user to define the following parameters
(a) Rolling Horizon Period
(b) Number of pieces in for a Piecewise Linear Cost Curve
Other changes include an improved test case file format reader that includes support for reading of load scenarios, and improved visualization of input and output data. The DAM interface includes an operation that solves a Security Constrained Unit Commitment (SCUC) formulation of the power system. The detailed formulation is listed in and in the chapter above. The SCUC formulation described in the previous chapter is implemented in Pyomo . Pyomo is a Python-based, open-source optimization modeling language with a diverse set of optimization capabilities. This formulation can be solved as a stochastic or deterministic formulation using the direct Pyomo solver. The PSST solver interface currently supports deterministic formulations; stochastic formulations are planned to be supported in the future.


