Game Interfaces And Wii Balance Board
Activity gaming systems provide a potentially attractive means to facilitate exercise and can be used as a tool to increase the activity levels in otherwise sedentary gamers. The commercial gaming systems are relatively inexpensive and can be located in a person’s home, making more convenient. Out of the activity gaming systems we chose the WBB as it is simple sophistication and a large user base with home and clinical based user interface for rehabilitation and exercise. Using the Wii Sports has been cited as a possible tool to enhance the process of rehabilitation. Anecdotally, the Wii is used in a number of settings within the National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom, such as for the elderly and patients with pathologies (stroke, amputation and Parkinson disease). The Wii has also been employed to facilitate rehabilitation at Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) centers in the United States. In 2007, seven VA facilities reported having a Wii, but by 2008, more than 80 facilities reported having at least one Wii. For patients with amputation, Nintendo requested that Ossur UK (Manchester, United Kingdom), a manufacture of prostheses for people with lower-limb amputation, produce an advisory document on the suitability of Wii exercise as a recreation or rehabilitation tool. These guidelines have been adopted by the British Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Amputee Rehabilitation, who produced a document aimed at guiding therapists using Wii Fit with patients with amputation in the NHS. A case study of an 89-year-old multiple faller who attended six 1-hour treatment sessions of Wii Bowling showed improved balance and possibly reduced the risk of falls.
The WBB is shaped like a household body scale, with a plain white top and under (Figure 1, Figure 2). It runs on four AA batteries as a power source, which can power the board for about 60 hours. The board uses Bluetooth technology for communications and COP sensors that are used to measure the user’s center of pressure (the location of the intersection between an imaginary line drawn vertically through the center of mass and the surface of the balance board) and weight.
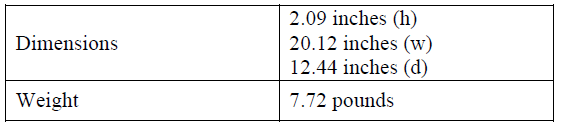
Table 1. WBB Dimensions and Weight
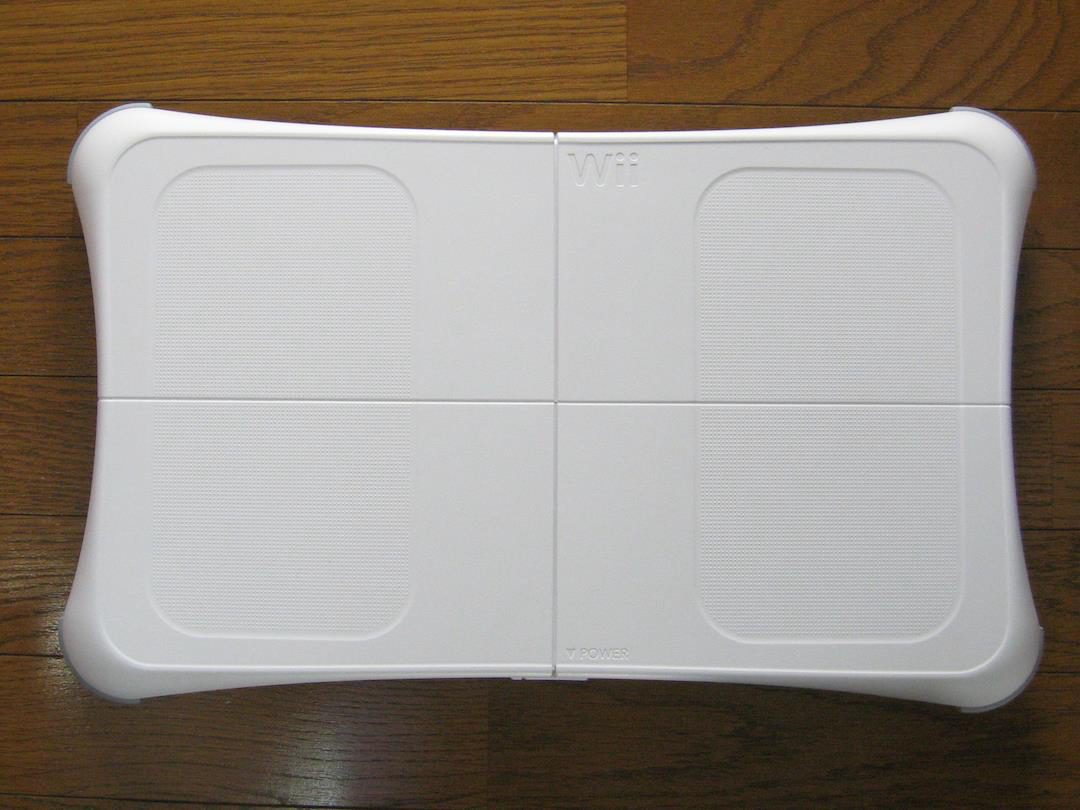

Figure 1. Wii balance board topside.

Figure 2. Wii balance board underside.
