supervisory control and data acquisition ( SCADA )
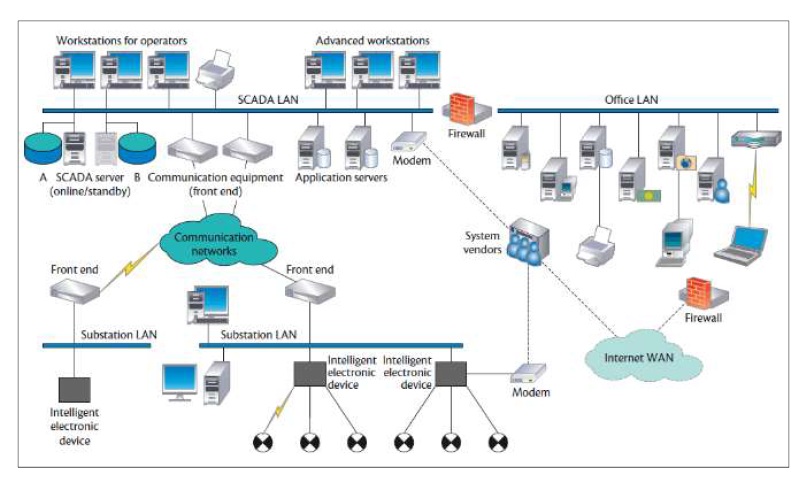
Figure 1: Shows a general SCADA system configuration and its components
SCADA systems are utilized to control geographically dispersed assets whenever centralized data acquisition is as essential as control. SCADA systems are ideal for distribution systems such as oil and gas, water systems distribution and collection systems, transportation as well as electrical transmission & distribution systems. SCADA systems integrate data transmission and data acquisition systems that are interfaced with HMI software to offer centralized control and monitoring of multiple process input and output. A SCADA systems is intended to collect information from the field, transfer the information to a centralized and computerized facility and graphically display the information to the operator. The displayed information allows operator to better control and monitor the entire system in real-time from a centralized location. The SCADA allows the control of the individual systems to be performed automatically or by manually entering operator commands .Typical SCADA hardware consists of a control server located at a control center along with telecommunication equipment such as telephone lines, radio, satellite or cable and field sites geographically distributed comprising of PLCs and remote terminal units (RTUs) for monitoring sensors and controlling actuators. The control server processes then stores information from the RTU input and output while the local process is controlled by the PLC or RTU. The telecommunication hardware facilitates the transfer of data and information between the RTUs or PLCs and the control server. The SCADA software is programmed to monitor process parameters and to know when these parameters are within acceptable operational ranges and the respective response that should be initiated when parameter values are outside acceptable ranges. Intelligent Electronic Devices (IED) for instance protective relays can communicate with the control server directly or to with a local RTU and may poll the IEDs in order to collect and pass data to the control server. SCADA systems are designed with high levels inherent of fault-tolerance and redundancy. However the redundancy may not be sufficient if there is a malicious attack . A control server and the communications routers are housed at the SCADA control center. Additional control center apparatus include the engineering workstation, HMI, as well as a data historian, with all components connected to a LAN. The SCADA control center accumulates and logs information collected by the different field sites, and displays information graphically to the HMI, and can also generate actions depending on detected events. The SCADA control center also has responsibility for centralizing alarms, reporting and trend analysis. The various field sites execute local monitoring of sensors and control of actuators. Field sites are frequently equipped with remote access capability that allows operators the ability to perform remote diagnostics or repairs typically over a dedicated dial-up modem or WAN connection. Both proprietary and standard communication protocols that run over network and serial communications are utilized for the transportation of information between the field sites and SCADA control center using telemetry techniques such as cables, telephone line, fiber, along with radio frequency such as microwave, broadcast, and satellite.


