ICS Communication Architecture and Modbus Communications
Modbus is a serial based communications protocol that was initially published by Modicon (Schneider Electric) in 1979 to be used with PLCs. It is robust and simple and is known as the de facto standard protocol for communication when connecting industrial electronic devices. The main strengths of the Modbus protocol are:
It was developed for industrial applications
It is royalty –free and openly published
Easy to maintain and deploy
Moves words or raw bits without putting restrictions on vendors Modbus allows communication between devices on a network and is usually connects a supervisory computer with remote terminal units (RTU) in a SCADA system. Modbus protocol development and updating is managed by the Modbus Organization . There are versions of protocol suitable for Ethernet and serial port as well as the Internet protocol suite. Devices intended to communicate over Modbus are each given a unique address. In MB+ and serial networks, only the node that is assigned to be the Master can initiate a command. For an Ethernet based Modbus network, any of the devices can send a Modbus command however only one master device typically does so. The address of the device (1 to 247) the command is intended for is contained in the Modbus command. Only the device that the command is intended for will respond to the command although other devices may receive it with the exception of specific commands that are broadcastable. Such commands to node 0 are acted upon without being acknowledged. Modbus commands include checksum information that allows recipients to detect errors in transmission. Basic Modbus commands can instruct an RTU to change register values, read or control I/O ports, as well as instruct the device to return vales stored in its registers. The Modbus protocol is used for control in every industry which makes it a prospective vector of attack to compromise industrial control systems.
Analysis of the MODBUS Protocol
Modbus was originally designed to work over a serial link like RS-232 or RS-485, it has evolved to an application layer messaging protocol for client/server communication. Due to its request/reply architecture it allows IP packets to be embedded on it and connect devices on different networks. Modbus is an application layer protocol at layer 7 of the OSI model. It can therefore relay over a set of different protocols. In 1999 an open Modbus TCP/IP specification was released. Modbus Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Internet Protocol (IP) allows Modbus information to be passed to TCP where additional information is attached and given to IP . A typical Modbus network will have a RTU or other type of device that will be monitored or controlled using ModbusTCP/IP The Modbus protocol is an application layer protocol and is designed to function at layer 7 of the OSI model. This allows it to function while stacked on top of different protocols as illustrated below.
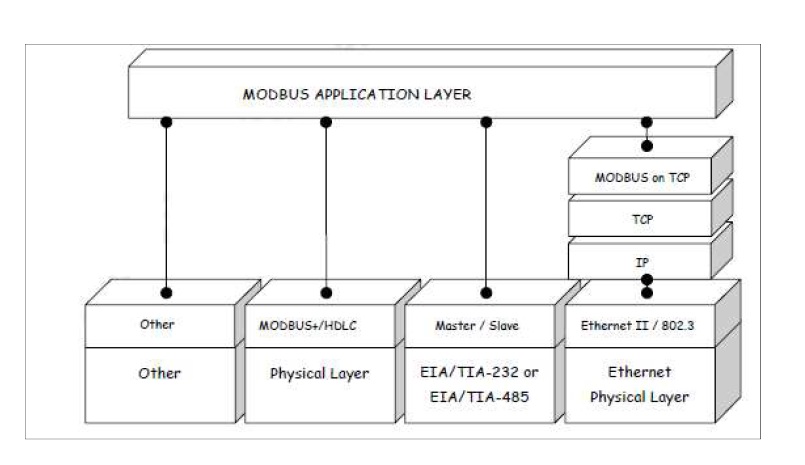
Figure 1 . Modbus Communication stack
The Modbus frame called an application Data Unit (ADU) which contains a one byte function code and a data field. ModbusTCP communication uses a client-server architecture with four types of messages; Request, Confirmation, Indication and Response .
MODBUS Request: Message sent on the network by the client to initiate a transaction.
MODBUS Indication: Request message received on the Server side.
MODBUS Response: Response message sent by the Server.
MODBUS Confirmation: Response message received on the client side.
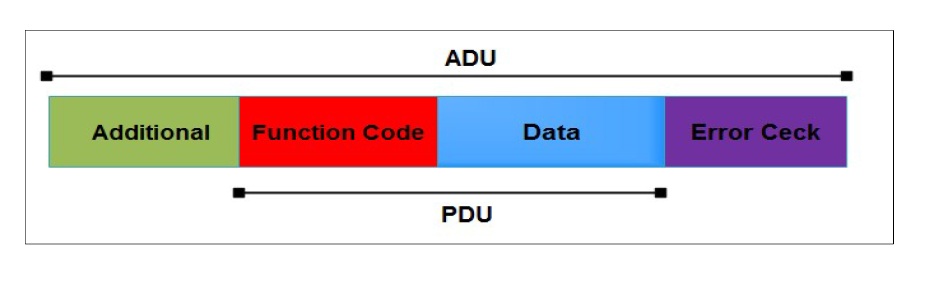
Figure 2 . MODBUS Frame (General)

