Electric vehicle Charging Standards
There are typically three levels of charging stations: Level 1, Level 2 and DC Fast Charge (DCFC) 1. These levels denote different charging rates of an electric vehicle’s battery. The use of higher level charging stations will dramatically reduce charging time, but the building cost is also significantly higher. The characteristics of three charging levels are summarized as follows.
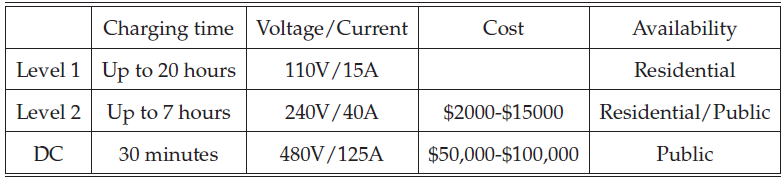
Table 1: EV charging classification
Level 1 charging is the most common form of battery recharging to satisfy all of a driver’s need. It provides charging from a standard residential 110 volt AC outlet. Most electric vehicle manufacturers include a Level 1 cord set so that no additional installation is required. On one end of the cord is a standard NEMA connector (for example, a NEMA 5-15, which is a common three-prong household plug) and on the other end is an SAE J1772 standard connector. The SAE J1772 connector plugs into the car’s J1772 charge port and the NEMA connector plugs into a standard NEMA wall outlet. The power consumption is approximately equal to that of a toaster, leading to about 4 miles of range per hour of charging. Overnight charging at 110V can replenish about 40 miles of driving range. However, a completely depleted battery could take up to 20-22 hours to completely recharge.

Figure 1: Level 1 charger
Level 2 equipment uses the same connector and charging port as level 1. However, level 2 equipment needs a dedicated electrical circuit to improve safety thus requiring professional electrical installation. The charging station can be installed in either residential houses or in public charging stations. The cost of installing a single port in a residential house is a little bit more than $1000, over half of which is the hard ware cost. The cost of installing a level 2 charging station in public stations varies from $2,000 to $15,000 with the number of ports, station features and brands. The power consumption of Level 2 charging is like a clothes dryer in the house. It will supply up to approximately 15 miles of travel for one hour of charging to vehicles with a 3.3kW onboard charger, or 30 miles of travel for one hour of charging for vehicles with a 6.6kW onboard charger. To fully charge an EV, it would take around 7 hours. Now, level 2 is the dominating class of public charging stations.
DC fast charging requires commercial grade 480V AC power circuits whose power consumption equals approximately 15 average size residential central air conditioning units. So it is only available in public charging stations. DCFC transforms the AC power to DC and supplies up to 40 miles of driving range for every 10 minutes of charging, or a full recharge in 30 minutes. Among the DCFCs deployed in the USA, there are three types of DC fast charging systems: SAE J1772 Combo used by Chevrolet and BMW, CHAdeMO used by Nissan, Mitsubishi, Toyota, and Fuji, and Tesla’s supercharger. The cost of a DC charging station is between $50,000 to $100,000 due to the expensive hardware and the frequent need to install a new 480V transformer.

